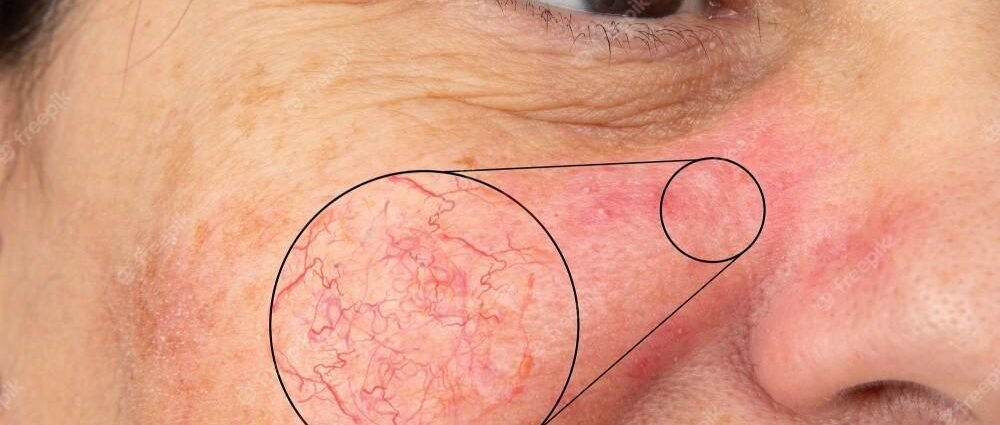
Rosacea is a chronic disease that affects the skin and sometimes also the eyes. It produces rash, redness, visible blood vessels, and the appearance of grains that can be confused with acne or allergic reactions.
This skin disease can affect anyone, but it is more common in middle-aged women with light skin, as their capillaries are more fragile. It affects the face alone, especially the cheeks, nose, forehead and chin.
What causes rosacea?
Although the causes of rosacea are not known exactly, it is known that there are some factors that aggravate the symptoms. For example, exposure to ultraviolet radiation without adequate protection, extreme temperatures, emotional stress, alcoholic and hot beverages, or very dry environments.
In addition, the use of masks during the COVID-19 pandemic can exacerbate this situation due to occlusion, low ventilation, and humidity. That’s what Dr. Ricardo Ruiz Villaverde, spokesman for the Spanish Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, assures that the use of the mask, which most of the population we have put most of the day, influences the appearance of two types of problems, especially seborrheic dermatitis and rosacea, or perioral dermatitis.
What are the symptoms?
– Face redness. The rosacea usually causes persistent redness in the central part of the face due to swelling of the small blood vessels of the nose and cheeks.
– Red and swollen bumps. In many cases, it is also common to develop acne-like pimples on the face that may contain pus.
– Eye problems. Irritated and dry eyes are another symptom of rosacea. Also, it’s common to have red and swollen eyelids.
Can rosacea be cured?
There is no cure for rosacea, but treatment can control and reduce signs and symptoms. First, it is important that if you suspect that you are suffering from it, it’s important to go to the dermatologist to confirm the diagnosis and start treating it before it evolves to more advanced stages.
First of all, it should be borne in mind that it can be prevented by the daily use of sunscreen, micellar water, and specific moisturizing creams, and taking care of the food. It is important to avoid alcoholic or very hot drinks, spicy meals, spices such as curry, cloves, or cumin, citrus fruits, and acidic vegetables such as tomatoes, red peppers, eggplants, beetroot, and radish.
There is also pharmacological treatment, always with prior consultation with the dermatologist, such as metronidazole or topical azelaic acid. Systemic treatment with antibiotics is indicated in cases of moderate or severe rosacea, in mild forms that do not respond to topical treatment, and in ocular rosacea. In addition, there are aesthetic treatments such as the vascular laser, which help close the small dilated blood vessels, causing a decrease in redness.
- Best Korean Skincare for Women in Their 40s
- Properties and uses of aloe vera in cosmetics
- What CBD is and what effects it has on your skin