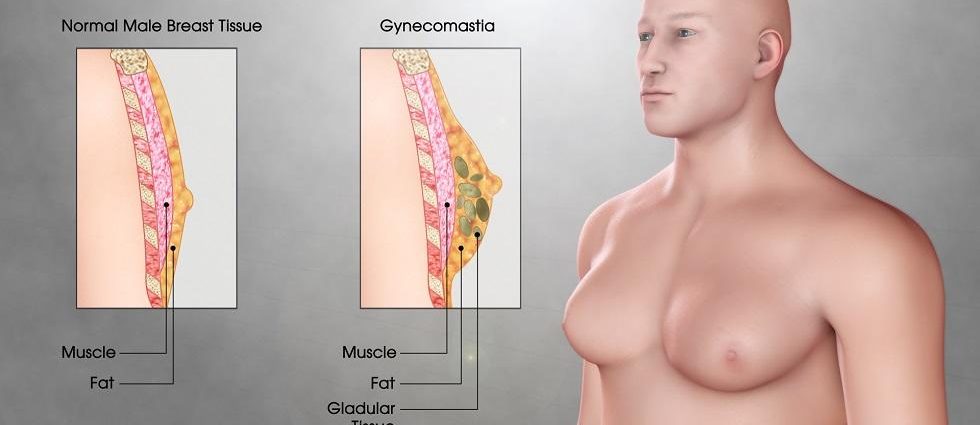
Gynecomastia, or male breast enlargement, is a condition that often carries heavy emotional and physical burdens. More common than many might think, it affects men from all walks of life, spanning various age groups. At its core, gynecomastia results from hormone imbalances, specifically when estrogen levels rise or testosterone levels fall. Understanding this condition is the first step toward addressing it, shedding light on the path to finding comfort and confidence in one’s own body. Whether it’s mild or severe, knowing the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available can make a significant difference.
Let’s dive deeper into what gynecomastia is, why it happens, and how those affected can seek relief and regain control over their lives.
Gynecomastia: Definition and Overview
Gynecomastia is a condition characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in males, a situation that can lead to considerable discomfort and self-consciousness. It is a common but often misunderstood issue that affects males of all ages, from newborns to the elderly. Unlike fat deposits from obesity, gynecomastia involves glandular tissue and can present in one or both breasts. Understanding this condition is the first step towards demystifying it and seeking appropriate treatment. The reasons behind gynecomastia are multifaceted, involving hormonal imbalances, certain medications, and underlying health conditions, making it critical to approach it with a comprehensive understanding.
Causes of Gynecomastia
Multiple factors can lead to the development of gynecomastia, with hormonal imbalance being the primary cause. Estrogen and testosterone, the sex hormones, when unbalanced, can trigger breast tissue growth. This imbalance may occur naturally during puberty, aging, or as a part of other health issues. Additionally, medications such as anti-androgens, antidepressants, and anabolic steroids can contribute to its development. Underlying health conditions like liver disease, kidney failure, and tumors can also lead to gynecomastia by affecting hormone levels. Recognizing these causes is crucial in identifying the best course of treatment and understanding that those affected are not alone in their experience.
Symptoms of Gynecomastia:
- Physical Symptoms
The primary symptom of gynecomastia is the enlargement of one or both breasts, which can present differently from one individual to another. Early signs include a lump of fatty tissue under the nipple that may feel tender or sore when touched. This enlargement may be uneven, with one breast appearing larger than the other. In some cases, the breasts may have a firm or rubbery feel, depending on the amount of glandular versus fatty tissue. It’s important to note that gynecomastia is different from lipomastia or “pseudogynecomastia,” which refers to fat deposits in the breasts due to obesity rather than the growth of breast tissue. Recognizing these physical symptoms is vital for early diagnosis and treatment.
- Emotional and Psychological Impact
The impact of gynecomastia extends beyond physical symptoms, often causing significant emotional and psychological distress. Men and boys with this condition may experience embarrassment, decreased self-esteem, and social isolation due to the appearance of their chest. It can especially be challenging during adolescence, a time already fraught with self-consciousness and social pressure. The psychological toll can manifest in various ways, from avoiding physical activities and social interactions to symptoms of depression and anxiety. Understanding and addressing these impacts is just as important as treating the physical symptoms. Affected individuals should be encouraged to seek both medical and psychological support to navigate these challenges effectively.
In closing, gynecomastia is more than just a physical ailment; it is a condition that can significantly affect a person’s quality of life through both its physical manifestations and the emotional burden it carries. Recognizing the symptoms, understanding its causes, and seeking appropriate treatment can greatly alleviate both the physical and psychological impacts of gynecomastia. If you or someone you know is experiencing signs of gynecomastia, it is highly advisable to consult with a healthcare provider for a comprehensive evaluation and to discuss the most suitable treatment options. Remember, gynecomastia is manageable, and with the right approach, individuals can recover from or effectively manage this condition and lead a confident, fulfilling life.
Diagnosis of Gynecomastia:
Understanding the cause of gynecomastia, a condition resulting in male breast enlargement, is critical for determining the most appropriate treatment. The diagnosis process involves a combination of medical examination, hormone testing, and sometimes additional imaging tests. Let’s delve into the primary steps that healthcare providers take to diagnose gynecomastia accurately.
- Medical Examination
The initial step in diagnosing gynecomastia involves a thorough medical examination. During this phase, the healthcare provider will inquire about any medical history, including medication use, as some medications can trigger gynecomastia. A physical examination is conducted to assess the extent of breast tissue enlargement and to differentiate between fatty tissue and glandular tissue, which is an important distinction in gynecomastia. Palpation helps in determining the texture and the exact areas of enlargement. Furthermore, the doctor will look for any signs of possible underlying conditions that could be contributing to the breast enlargement.
- Hormone Testing
One of the primary causes of gynecomastia is an imbalance between the hormones estrogen and testosterone. To investigate this potential imbalance, doctors often order hormone tests, typically involving blood samples. These tests are crucial as they help in identifying any hormonal abnormalities that might be at the heart of the condition. Depending on the findings, further tests might be recommended to scrutinize the liver, kidneys, and thyroid, as these organs are instrumental in hormone production and regulation.
Treatment Options for Gynecomastia:
Once gynecomastia has been diagnosed, there are several paths to address and manage the condition, ranging from non-surgical treatments and lifestyle adjustments to surgical interventions. The choice of treatment largely depends on the severity of the condition, its cause, and the patient’s preferences.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatments are often the first line of action, particularly in cases where gynecomastia is mild or if it’s thought to naturally resolve over time. These include:
- Medication: Certain medications that block estrogen, akin to those used for breast cancer treatment, may be prescribed. In addition, if gynecomastia is a side effect of another medication, switching drugs might be an option.
- Hormone Therapy: If gynecomastia is due to a significant imbalance in hormones, hormone replacement therapy might be considered to restore balance.
These approaches can be effective, especially in addressing the underlying hormonal imbalances or if the condition is in its early stages.
Surgical Interventions:
For more severe cases or when gynecomastia doesn’t improve with non-surgical treatments, surgery might be recommended. There are two main types of surgical procedures used to treat gynecomastia:
- Liposuction: This procedure involves the removal of breast fat but does not affect the breast gland tissue.
- Mastectomy: This surgery involves the removal of the glandular breast tissue, usually performed endoscopically with minimal scarring.
Surgery can provide a permanent solution to gynecomastia, significantly improving the physical appearance and self-esteem of affected individuals.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies:
In addition to medical treatments, making specific lifestyle changes can help manage the symptoms of gynecomastia and, in some cases, may also aid in its resolution:
- Diet and Exercise: Adopting a healthy diet and engaging in regular exercise can help reduce body fat, which might decrease the appearance of enlarged breasts.
- Avoid Certain Substances: Limiting or avoiding alcohol, steroids, and any drugs known to trigger gynecomastia can be beneficial.
- Wear Supportive Garments: Compression shirts can provide temporary aesthetic solutions, helping to flatten the chest appearance.
While lifestyle changes alone may not cure gynecomastia, especially in moderate to severe cases, they play a crucial role in overall treatment, promoting a healthier lifestyle and potentially minimizing the risk of recurrence.
Deciding on the right treatment for gynecomastia involves a careful consideration of the condition’s cause, its severity, and the patient’s desired outcome. It’s paramount for individuals suffering from this condition to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate course of action. With the right treatment plan, individuals can achieve significant improvement in their physical appearance and regain their confidence.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts:
In wrapping up our discussion on gynecomastia, we’ve navigated through the key areas surrounding this condition, from the causes and symptoms to the wide array of treatment options available. Understanding that male breast enlargement stems largely from hormone imbalance provides a foundation for addressing and managing the condition effectively.
Gynecomastia, while potentially embarrassing and uncomfortable for those experiencing it, is generally treatable, either through lifestyle adjustments, medication, or surgery, depending on the underlying causes and severity of the condition. It’s crucial for individuals suffering from gynecomastia to consult healthcare professionals to explore the most suitable treatment path tailored to their specific needs.
- Approach a healthcare provider for a comprehensive evaluation.
- Consider all treatment options available, weighing the benefits and drawbacks of each.
- Remember, you’re not alone; support groups and counseling can offer valuable emotional support and advice.
Finally, with the advancements in medical science, the outlook for managing and treating gynecomastia is more promising than ever. Embracing the journey towards treatment with an open mind and a proactive approach can lead to significant improvements in both physical appearance and psychological well-being. Together, let’s break the stigma and foster a supportive community for those affected by gynecomastia.