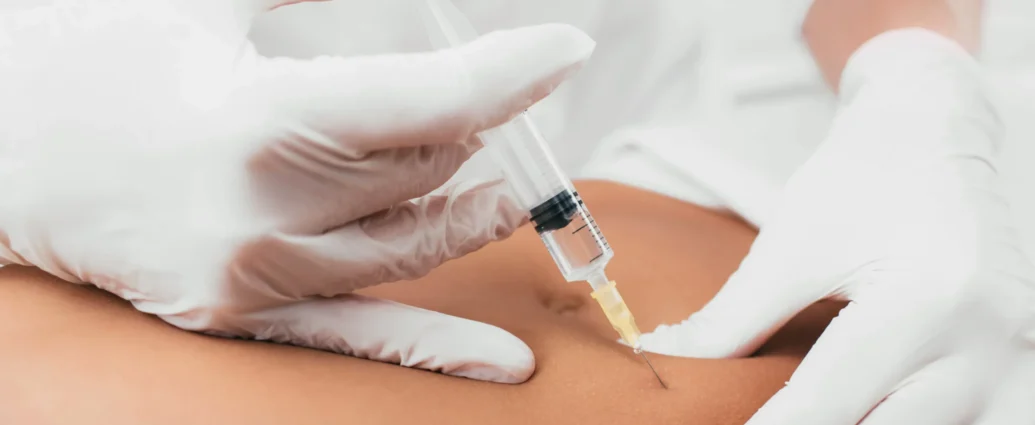
Compounded tirzepatide is a specialized formulation of the medication tirzepatide, which is primarily employed in the management of type 2 diabetes and obesity. Tirzepatide itself is a novel active compound that belongs to a class of drugs known as GLP-1 receptor agonists. It exerts its therapeutic effects by mimicking the action of incretin hormones, which play a significant role in glucose metabolism. By stimulating insulin secretion in response to elevated blood sugar levels while concurrently suppressing glucagon release, tirzepatide helps regulate glucose levels effectively.
Compounding refers to the process of tailoring medications to meet individual patient requirements. In the case of compounded tirzepatide, pharmacists create unique formulations that may combine tirzepatide with other compounds or adjust its dosage form. This customization allows healthcare providers to address specific clinical needs that may not be met by standard commercial preparations. For example, patients who experience difficulties with traditional injection methods may benefit from a compounded oral form, thus enhancing adherence to treatment.
The unique aspect of compounded tirzepatide lies not only in its formulation but also in its ability to provide patients with doses of tirzepatide that are more personalized. Healthcare professionals can modulate the strength and delivery mechanism based on factors such as patient tolerance, comorbidities, and individual health goals. Consequently, compounded tirzepatide serves as a flexible option for those seeking effective management of conditions like obesity and type 2 diabetes, facilitating a more tailored approach to treatment.
The Safety of Compounded Tirzepatide
Compounded tirzepatide, a novel therapeutic agent primarily indicated for managing weight and related metabolic disorders, raises essential safety considerations that warrant comprehensive evaluation. Clinical studies focusing on tirzepatide have highlighted its safety and efficacy; however, the safety profile of compounded versions remains less extensively researched. While general findings indicate a favorable safety margin, the risks associated with compounded formulations can differ significantly based on the compounding process and the expertise of the pharmacy involved.
Potential risks and side effects of compounded tirzepatide may include gastrointestinal disturbances, such as nausea and diarrhea, alongside the possibility of developing allergic reactions. Moreover, variations in medication strength due to compounding errors can pose additional risks, making it crucial for patients to utilize certified compounding pharmacies that adhere strictly to regulatory standards. Such pharmacies ensure the medication is prepared under controlled conditions, using high-quality ingredients, ultimately minimizing the likelihood of contaminants and inconsistencies.
Patients considering compounded tirzepatide should be well-informed about the guidelines for usage. It is advisable to undergo a thorough medical consultation to evaluate personal health histories and contraindications. Monitoring is crucial following the initiation of treatment, enabling the healthcare provider to assess the patient’s response and adjust dosage as necessary. Regular follow-ups and open communication with the healthcare provider are also essential in managing any emerging side effects effectively.
In considering compounded tirzepatide, patients must remain vigilant and proactive about their safety. By obtaining the medication from certified pharmacies and adhering to prescribed guidelines, individuals can significantly enhance their treatment experience while minimizing potential risks associated with the use of compounded formulations.
Understanding Tirzepatide Dosage: A Comprehensive Chart
The administration of tirzepatide necessitates a nuanced understanding of appropriate dosing for various patient populations. The recommended starting dosage for most adults is typically set at 2.5 mg. Depending on the patient’s individual response to the medication, healthcare providers may gradually increase the dose. Adjustments are essential to optimize therapeutic outcomes and minimize potential side effects. For many patients, an increase to 5 mg or higher may be appropriate over several weeks, with some patients requiring doses as high as 10 mg or 15 mg after thorough clinical evaluation.
For elderly patients or those with compromised kidney function, careful consideration is warranted. The starting dosage may need to be lower, and the titration process should be approached conservatively. It is crucial to monitor these patients closely as they may be at a higher risk for adverse reactions due to age-related physiological changes and diminished renal clearance. Therefore, a personalized medication plan based on comprehensive health assessments is imperative.
When discussing compounded tirzepatide, practitioners should also note that the dosing may differ from the standard formulations. Compounded forms are often tailored to meet specific patient needs, which may include alterations in concentration or delivery methods that are not available in standard preparations. Healthcare professionals should collaborate with compounding pharmacies to ensure that dosages are accurate and that compounding adheres to regulatory standards.
The importance of individualized medication plans cannot be overstated. Patients may respond differently to the same dose of compounded tirzepatide, which makes it essential for healthcare providers to continuously evaluate dosage effectiveness and safety at each follow-up visit. This patient-centric approach can help enhance treatment outcomes and improve overall satisfaction with the therapeutic process.
Is Compounded Tirzepatide Going Away? Exploring Future Trends
The future of compounded tirzepatide is a topic of growing interest, particularly amid regulatory shifts and evolving market demand for compounded medications. As healthcare systems continue to adapt, many factors might influence the availability of compounded formulations of tirzepatide. Firstly, regulatory changes play a significant role in shaping the future of compounded drugs. Legislative bodies often amend guidelines governing the compounding of medications to enhance safety and efficacy, which could impact how tirzepatide is formulated and dispensed. This dynamic regulatory environment suggests that while compounded tirzepatide is currently available, its status may evolve based on regulatory scrutiny.
Market demand for compounded medications remains robust, driven by patients seeking customized treatments catering to their specific needs. This ongoing demand for personalization in medication not only supports the survival of compounded tirzepatide but also encourages pharmacies to remain proactive in offering it. However, potential shortages in pharmaceutical supplies, whether due to manufacturing constraints or ingredient availability, could affect the accessibility of compounded therapies. In light of this, it is crucial for patients and healthcare providers to stay informed about supply chain issues that might arise, which could lead to temporary shortages even in substances like tirzepatide.
Additionally, ongoing research into both the therapeutic uses and the safety profile of compounded tirzepatide could affect its future availability. As scientific understanding of the drug improves, opportunities may arise for more robust formulations or novel applications. This advancement could lead to more consistent availability, or conversely, if adverse effects are noted in clinical settings, it might provoke regulatory tightening that impacts accessibility. Patients and providers alike should prepare for these potential developments, as the landscape surrounding compounded tirzepatide may shift, refining access and application in the coming years.
Comparing Compounded and Commercial Tirzepatide
Tirzepatide, originally developed and marketed as a commercial medication, has gained traction within the medical community for its multifaceted approach to treatment, especially in diabetes management. However, compounded tirzepatide offers an alternative that addresses specific patient requirements. At the core of the comparison between these two variants lies their formulation. Commercial tirzepatide comes in a standardized dosage form, providing a reliable and consistent treatment option for patients. In contrast, compounded tirzepatide allows healthcare practitioners to customize the medication according to individual patient needs. This flexibility can include adjustments in dosage, formulation, or even the addition of other active ingredients, thereby catering to unique health circumstances.
The customization capability of compounded tirzepatide proves beneficial for patients who may experience side effects with commercial formulations or those who require specific doses that are not commercially available. Such bespoke preparations enable clinicians to tailor therapies based on a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s health profile, potentially enhancing treatment efficacy. Furthermore, patients with allergies to certain excipients or inactive ingredients found in commercial tirzepatide can find relief through compounded options, where these can be omitted or replaced based on necessity.
Accessibility also plays a crucial role in the comparison. While commercial tirzepatide might be readily available in many pharmacies, compounded tirzepatide often presents a viable alternative for patients seeking a specific formulation that addresses their medical needs more appropriately. However, it is important to recognize that compounded medications are typically not subjected to the same rigorous FDA approval processes as their commercial counterparts, leading to varying levels of quality and efficacy. Thus, while compounded tirzepatide offers unique advantages in terms of customization and flexibility, the decision to utilize them should be made with careful consideration of potential risks and benefits.
Patient Experiences: Testimonials and Case Studies
The narrative surrounding compounded tirzepatide is greatly enriched by the testimonials and case studies of individuals who have integrated this medication into their treatment plans. These anecdotal accounts provide valuable insights into both the efficacy and potential drawbacks of this emerging therapeutic option. Many patients report that compounded tirzepatide has significantly improved their quality of life by aiding in weight loss and enhancing metabolic health. One patient, who struggled with obesity for years, shared that after incorporating compounded tirzepatide into their regimen, they experienced a steady reduction in body weight, which was complemented by a boost in energy levels and overall physical well-being.
Conversely, it is equally crucial to discuss the experiences of those who encountered challenges with this medication. A few individuals have expressed concerns about side effects, such as gastrointestinal discomfort, which included nausea and diarrhea. While these adverse effects are not universal, they highlight the importance of monitoring when first beginning treatment. A nuanced case study revealed that a patient discontinued use after experiencing consistent side effects that hindered their daily activities, underscoring the need for personalized medical guidance.
Healthcare Professionals’ Perspective on Compounded Tirzepatide
Healthcare professionals play a pivotal role in understanding and evaluating the effectiveness and safety of compounded tirzepatide. Pharmacists, endocrinologists, and general practitioners collaborate to create a comprehensive treatment strategy that addresses their patients’ unique needs. In recent years, compounded tirzepatide has emerged as an alternative therapeutic option for managing conditions such as obesity and type 2 diabetes. Clinicians are increasingly leveraging this treatment by closely monitoring its therapeutic outcomes and potential side effects.
Pharmacists are instrumental in preparing compounded tirzepatide formulations that adhere to individual patient specifications. They ensure that the production process aligns with safety protocols and regulatory standards. By consulting with physicians about dosage adjustments and contraindications, pharmacists contribute significantly to optimizing the treatment for patients. Their expertise in medication management helps mitigate risks associated with compounded medications.
Endocrinologists, who specialize in hormones and metabolic disorders, also play a vital role. They assess the clinical efficacy of compounded tirzepatide, analyzing data from various patient demographics. Their guidance on dosing regimens is crucial for maximizing therapeutic benefits while minimizing adverse reactions. Moreover, they educate patients on the importance of lifestyle modifications in conjunction with medication, thereby fostering a holistic approach to treatment.
General practitioners serve as the primary point of contact for patients seeking information about compounded tirzepatide. They evaluate a patient’s overall health status, making informed decisions about whether compounded tirzepatide is appropriate based on individual medical history and current medication use. By providing thorough evaluations and facilitating open discussions, general practitioners empower patients to make informed choices regarding their treatment options.
The collaboration among these healthcare professionals ensures that the integration of compounded tirzepatide into treatment plans is conducted safely and effectively, ultimately benefiting patients in their pursuit of health and well-being.
Regulatory Insights on Compounded Medications
The regulatory landscape for compounded medications is shaped by various guidelines and compliance measures aimed at ensuring patient safety. Compounding pharmacies, which prepare customized medications tailored to unique patient needs, operate under specific regulations enforced by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and state pharmacy boards. Compounded tirzepatide, a novel medication used for treating conditions like obesity and diabetes, exemplifies the need for rigorous oversight due to its specialized formulation.
According to FDA guidelines, compounded medications must meet certain standards to ensure their quality, potency, and safety. The FDA aims to prevent the misuse of compounding practices while still allowing flexibility for pharmacies to create medicines tailored to individual patients when commercially available alternatives are insufficient. Compounded tirzepatide, for instance, must comply with these regulations to guarantee its effectiveness and safety for patients requiring personalized dosages or delivery methods.
Compliance issues may arise when pharmacies fail to adhere to established guidelines. Non-compliance can lead to risks associated with poor-quality products, including contamination, incorrect formulation, or inadequate dosing. In relation to compounded tirzepatide, pharmacies must ensure that all ingredients are properly vetted and sourced from reputable suppliers. Regulatory oversight is paramount in maintaining a high standard of practice within the realm of compounded medications.
Compounding pharmacies play a critical role in this regulatory framework, providing the necessary infrastructure to produce specialized treatments while adhering to safety standards. Regular inspections and stringent quality assurance protocols help ensure that compounded tirzepatide, like all compounded medications, meets required efficacy and safety benchmarks. Understanding the regulations governing compounded medications can empower patients to make informed choices about their treatment options, balancing the need for tailored therapies with an awareness of safety considerations.
Conclusion: The Future of Compounded Tirzepatide and Patient Care
As we navigate the complexities surrounding compounded tirzepatide, it is evident that this medication holds significant potential for patient care, especially in managing conditions like obesity and diabetes. Throughout this discussion, we have analyzed the safety parameters, dosing considerations, and the implications of individualized treatment regimens. The importance of understanding the specific needs and health profiles of each patient cannot be overstated, as it allows for the formulation of tailored therapies that can enhance treatment outcomes.
The continuous evolution of compounded tirzepatide signifies not only advancements in pharmaceutical science but also highlights the critical nexus between technology and personalized medicine. Ongoing research will be pivotal in further elucidating the benefits and risks associated with this medication, including its long-term efficacy and safety in various populations. It is essential for healthcare providers to stay informed about new findings and developments to make educated decisions that benefit their patients.
Equally important is the role of patient education in this evolving landscape. Patients should be empowered with knowledge about compounded tirzepatide, understanding both its potential advantages and associated risks. Clear communication between patients and healthcare providers fosters an environment conducive to shared decision-making, ensuring that individuals feel supported and informed throughout their treatment journey. This partnership will be crucial as we move toward a more individualized approach to healthcare.
In summary, the future of compounded tirzepatide in patient care looks promising, marked by an increased emphasis on personalized medication strategies. As research progresses and healthcare practices adapt, it is imperative that we remain committed to enhancing patient outcomes through education, collaboration, and informed decision-making to effectively harness the benefits of this innovative treatment.