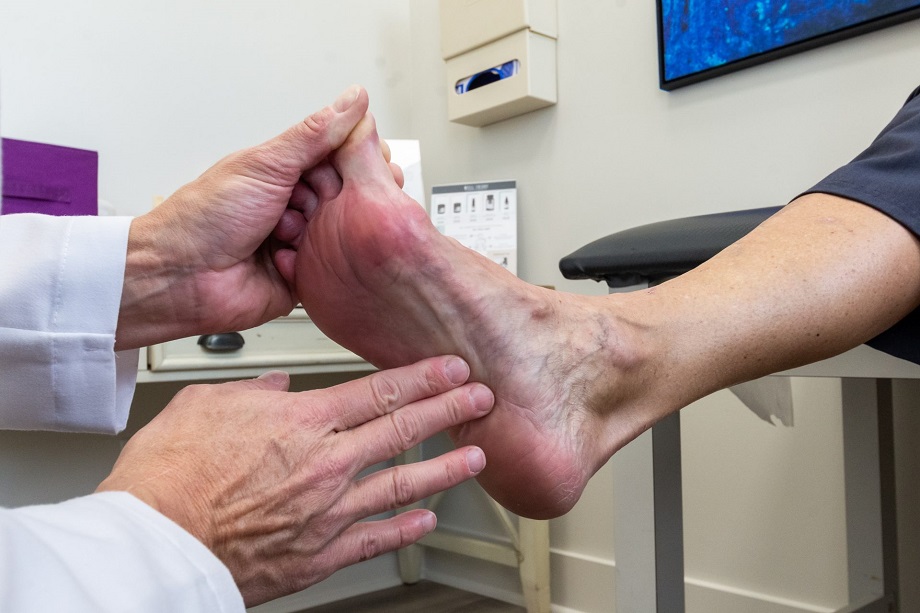
The foot is one of the most important elements of the human body. Especially for the athlete. Its function is simple: it sustains us and generates the bipedal movement. Thus, any pathology or discomfort in it can lead to other problems of greater caliber and worse diagnosis.
In both athletes and people over 45 years of age who do not exercise regularly, it is very common to develop one of the most painful lesions: plantar fasciitis. This is one of the most common foot pathologies faced by podiatrists. According to the Official College of Podologists, at least 20% of the Spanish population will suffer from plantar fasciitis in their lives.
Do you want to know if the pain you feel when you start going corresponds to plantar fasciitis? Keep reading.
What Is Plantar Fasciitis?
Plantar fasciitis occurs because the plantar fascia, the tissue that connects the heel with the fingers and protects the muscle of the foot, is responsible, among other functions, for absorbing the impact of the footprint and returning the effort and energy to the muscles of the leg, is inflamed and produces very intense pain by supporting the foot. Especially in the first six months when he shows up.
Once this first phase of morning pain is overcome by taking the first steps, it becomes a recurring nuisance for the rest of life. When presented, it limits the physical activity that the person can perform.
Most cases of plantar fasciitis occur in the insertion area between the fascia and heel.
The Profile Of A Sufferer Of Plantar Fasciitis:
Problems with the planting fascia are very common among athletes, especially among those who practice impact sports and high demand for the articulation of the foot (football, volleyball, for example).
Also, women who regularly wear high-heeled shoes are more likely to suffer from some episode of plantar fasciitis as the foot posture causes a shortening of the posterior leg muscles. Hence, an alternation between the most pronounced heel, wedges, and flat shoes is recommended. However, in no case should a sudden change be made, as the tension on the tendon can lead to acute tendinitis in the Achilles tendon.
Difference Between Fasciitis And Calcaneal Spur:
It is not unusual to confuse plantar fasciitis with the calcaneus spur when the first symptoms occur in the form of acute pain when the footrests. And it is that plantar fasciitis and the calcaneus spur have a fairly similar symptomatic picture. However, once the radiological test of the foot has been performed, we will observe subtle but determining differences. The calcaneus spur is produced by a calculus calcification or heel bone that causes it to grow – and pressure the fascia and muscles, generating pain. Plantar fasciitis generates pressure in the fascia but without calcification. In both cases, the sooner we go to the specialist for his proper diagnosis, the sooner we will start treatment and the better results we can have
Causes
Plantar fasciitis implies that the fibrous ligament from which the fascia is made tears the tissues, causing inflammation and pain. There is no single cause to explain the appearance of fasciitis. It occurs both in people who have remained at rest for a long period and in those who do a lot of physical activity. The type of footwear and footprint also has a lot to do with the appearance of this painful foot pathology.
Also, not wearing shoes appropriate to the activity to be performed is another potential origin of plantar fasciitis; if you have sprained and have not completely healed it, you will tend to force the posture of the foot for pain, which will result, in turn, in fasciitis. Even muscle overload seems to be related to pain in the fascia.
Symptoms
In any case, you’ll notice a very particular pain, as if you’re walking on crystals. Even putting on the shoes is a misery. This acute pain is shown to be more intense in the first steps taken when you get up and walk a few steps. This is because, during the night, the fascia relaxes and is shorter. Once you start walking, the fascia wakes up and the pain refers.
How To Prevent Plantar Fasciitis?
Before you get to this situation, you can perform a series of routines and exercises that will help you prevent plantar fasciitis, such as stretching the muscles of the foot and lower leg, both before playing sport and when you get up.
Of course, always wearing shoes to walk home will be a reducing element of discomfort and possible relapses.
The Diagnosis
The first symptoms must appear be the specialist to assess the situation and face treatment as soon as possible. Otherwise, the inconvenience will become more acute, even becoming an impediment to moderate physical activity.
The scan includes identifying when the pain is being felt and if there has been any event that may have triggered it. Then a study of the march and the footprint is carried out to check the possible points of stress and tension on the fascia. Older, the X-ray is done to confirm that it is not a spur, a cyst, or even a fracture. Finally, the foot ultrasound reveals whether the fascia is thickened, has tears, or has scars of tears.
Recommended Treatments For This Foot Pathology
The first and most important step to be taken when the diagnosis of plantar fasciitis is confirmed is to maintain absolute rest. For older people, the physician may prescribe some kind of anti-inflammatory to combine with physiotherapy sessions. Once neutralized, it would be no wonder that functional bandages or custom templates are prescribed. To this end, the patient will undergo a biomechanical study of the march.
When plantar fasciitis is controlled, it is important to acquire a series of routines that help to strengthen what has been achieved and avoid relapses. For example, it is highly recommended to stretch the twin and the sole or massage the area with anti-inflammatory ointment.
Only in the end, and when none of the above has had an effect, can intervention be proposed.