Cystitis or urinary tract infection is one of the most common infections after respiratory infections. An infection with a high prevalence among women, although for men they often have more complications.
The age range in which urinary infections are more common is between 15 and 50 years of age, sexual activity is one of the risk factors by multiplying by more than 3 the chances of infection. For women over 50, the risk factor is due more to the shortage of estrogen.
Knowing what cystitis, causes, symptoms, and treatments and maintaining very careful intimate hygiene are basic to prevent both their onset and chronification.
What Is It?
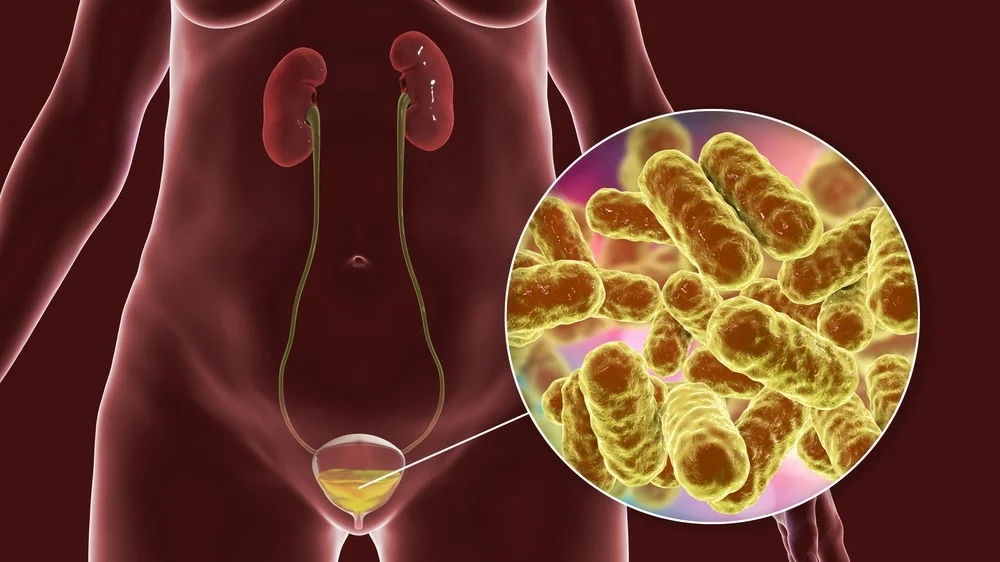
Urine or urinary tract infections (UTIs) are infections caused by microorganism invasion in this area, although this expression includes infections from anywhere in the urinary system, from the kidney to the urinary bladder. The attack of these bacteria or microorganisms occurs through the urinary tract, penetrating the urethra, ascending from there to the bladder and producing the infection; or by the blood flow.
Microorganisms that cause these infections are usually bacteria, fungi, viruses, or parasites, being common, in at least 80% of cases, that the infection is caused by Escherichia coli, a bacteria that is housed in the intestine.
Urinary infections can be of two types:
- Lowway infections: cystitis, urethritis, and prostatitis.
- Highway infections: acute pyelonephritis, acute bacterial nephritis, intrarenal abscess, and perinephric abscess.
Causes
The causes of cystitis are varied and may be enhanced or aggravated by certain risk factors. Thus, as we have pointed out, age and sex are elements to be taken into account when studying the incidence of urinary infections.
Young women are often the most affected by this type of infection, especially if they have a family history, have sex, and often use spermicide. For their part, young men do not usually suffer from this type of infection, and are often associated with their sexual activity.
Postmenopausal women are also often affected by this type of infection. In men over 50 years of age, they are usually associated with bacterial infections in the prostate.
The impact is very similar on both sexes from the age of 50 and always related to their stay in hospital, urinary incontinence, and the use of compresses and diapers for adults. Urine losses are a breeding ground for bacterial growth, in addition to the fact that moisture in the genital area favors this process.
Other causes that may enhance or aggravate urinary infections include:
- The pregnancy.
- If there are malformations of the urinary tract or obstructions of the urine flow such as a dilated prostate, or stones in the kidney.
- To suffer from diseases such as diabetes, neurological diseases, and cancer, among others.
- With little hygiene at the time of the bath in swimming pools and beaches, it is advisable to quickly change wet swimwear clothes to stop the proliferation of microorganisms.
- Immunal depression.
Symptoms
Symptoms of cystitis vary depending on the area where the infection is located. Either way, there are several very common symptoms such as:
- Pain and stinger when urinating or dys fur.
- Continuous urge to urinate and not urinate at all despite having the sensation of a full bladder.
- Get up frequently at night to urinate or nocturia.
- Dark and murky orina, as well as having an intense smell.
- Blood in the urine or hematuria.
- In women, some redness of the vulva area and itching in the vaginal area can also be perceived.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- High fever in case the infection gets worse and reaches the kidneys.
- Shaking chills.
- Intense pain on the side or in the kidney area.
- Women may also feel pressure in the area of the pubic bone, while men may notice some dilation in the rectal area.
- The symptoms are very similar in the case of children, and they are also common to have less appetite and more irritability.
Prevention
One of the most effective ways to avoid cystitis is to take water daily, at least two liters, and urinate whenever you feel like it, without retaining urine. A balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle in which certain intimate hygiene aspects are taken into account are also basic.
Among the most effective preventive measures to reduce the chances of cystitis are:
- It is recommended to urinate before and after each sexual act to eliminate infectious agents that may have been introduced.
- Choose carefully condoms, type, and material from the diaphragm and sperm creams if you have a certain predisposition to urinary infections. It is advisable to go to a specialist to consult the method of contraception that best suits you.
- Using lubricating creams during sex as postcoital vaginal irritation is a common cause of infections.
- Do not resort to vaginal shower as a method of contraception.
- Wear cotton underwear and avoid too tight and fiber clothing.
- Try to change the swimsuit or bikini after the bathroom and always wear clean and dry swimwear. Try not to catch a cold.
- Use a neutral pH gel for the intimate areas dermatologically tested and keep the area clean and dry.
- Frequent change of diapers in children and adults to prevent the proliferation of bacteria.
- Frequent changes of compresses during menstruation, also increase the hygiene of the area.
- Avoid constipation.
- Consumption of food infusions and supplements to help prevent infections. Red blueberries and Goji berries are very effective in preventing infections.
Treatments
After a diagnosis through tests ranging from physical examination to analysis and cultivation of urine, vaginal fluid or urethral fluid, a cystoscopy, an abdominal ultrasound, or a urography, the specialist will be able to tell us where the infection is located and what is the most adjusted treatment to stop the infection and the annoying effects that accompany it.
The most common treatment is an antibiotic treatment in the case of a bacteria, or an antiviral, originating if they are caused by a virus. Depending on the type of bacteria and if there are more associated complications, longer treatment will need to be addressed. Once the treatment is completed, the specialist will proceed to do a new analysis to determine whether there are no longer traces of bacteria in the urinary tract.
If the infection is the result of physical obstruction, surgery may be necessary to remove the stone or correct physical anomalies that may also be favoring the chronification of urinary infections.